 ↑他グループへはアイコンをクリック
↑他グループへはアイコンをクリック
軽金属材料グループ
Light-weight Metallic Materials Group
研究概要
近年の省エネルギー・省資源、さらには京都議定書発効による二酸化炭素排出量の削減といった社会的要請から、飛行機、鉄道車両や自動車などの移動用構造部材の軽量化が盛んに検討されています。このような背景のなか、実用金属材料で軽量なアルミニウム合金やマグネシウム合金の内部組織をナノ〜ミクロ〜マイクロの階層的な組織制御により、使用に際して安全で壊れにくい材料や、新しい特性や機能をもつ材料の開発に取り組んでいます。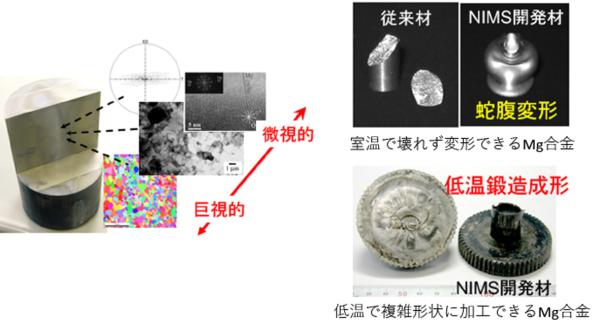
塑性変形機構理解に基づく高強度・高靭性化
マグネシウム合金は、結晶構造 (=六方晶構造) に起因して、塑性変形時に双晶を形成することで知られています。しかし、双晶と母相の界面は、き裂の進展経路になりやく、マグネシウムの脆さの要因です。ここでは、原子・ナノレベルでは母相に分散する粒子の界面や形態の制御、ミクロレベルでは結晶粒界や結晶粒サイズの制御、マイクロレベルでは底面の配向を、各々階層的に制御することで、強度特性を損なわず、靱性の改善に成功しています。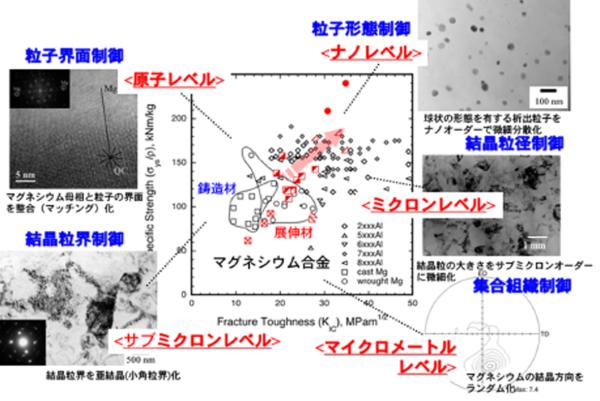
メンバー
染川 英俊 SOMEKAWA Hidetoshi
構造材料研究センター 材料創製分野
軽金属材料グループ グループリーダー




