 ↑他グループへはアイコンをクリック
↑他グループへはアイコンをクリック
腐食研究グループ
Corrosion Research Group
メンバー
片山 英樹 KATAYAMA Hideki
構造材料研究センター 副センター長
村瀬 義治 MURASE Yoshiharu
構造材料研究センター 材料評価分野
腐食研究グループ 主任研究員
構造材料,耐食性評価,結晶構造解析,顕微鏡解析,電気化学試験
門脇 万里子 KADOWAKI Mariko
構造材料研究センター 材料評価分野
腐食研究グループ 主任研究員
研究概要
金属材料の腐食は、構造物の劣化・損傷を引き起こす要因の一つであり、経済的な損失につながります。腐食研究グループでは、多くの腐食課題の解決のため種々の環境下にさらされた金属材料の表面および界面で生じる腐食劣化挙動について調査しています。さらに、それらの機構解明を通してさまざまな使用環境における金属材料の信頼性や耐久性の向上に貢献することを目指しています。
専門分野・研究対象
1. 鉄鋼材料の大気腐食モニタリング技術の高度化と非破壊腐食リスク予測技術の確立
これまでに整備された社会インフラを長期間安全に使用するためには、今後、補修や更新などで莫大な費用がかかることが試算されており、従来の事後保全型メンテナンスから予防保全型への転換が求められています。予防保全型メンテナンスにおいて重要となるのは正確な現状把握とリスク予測であり、本テーマでは、現状把握のための鉄鋼材料の大気腐食速度のモニタリング技術の高度化と簡便な非破壊評価法による腐食リスク予測技術の確立を目指しています。
2. SKPFM-EBSD-EDS解析による腐食挙動評価
走査型ケルビンプローブフォース顕微鏡 (SKPFM) 、走査型電子顕微鏡における電子線後方散乱回折 (EBSD) 法ならびにエネルギー分散型X線分光 (EDS) 法を用いて、構造材料の結晶組織に依存する腐食挙動解析を行っています。SKPFMでは、表面電位変化を検知することにより腐食発生箇所をマッピング表示し、EBSDでは結晶構造解析により耐食性評価を行い、EDSでは元素分析による介在物や元素偏析を伴う腐食反応を検知します。本研究は、これら3つの異なる解析手法を連携し、耐食性に優れた構造材料設計指針を得ることを目的としています。
3. 金属材料の耐食性を極限まで向上させる新規表面処理技術の開発
意図せぬ腐食損傷や事故のリスクを極限まで低減し、安心して使用できるステンレス鋼表面に改質するための表面処理技術を開発しています。特定の処理溶液中で、新規開発した条件で通電することで、腐食の起点となる、鋼表面に露出した欠陥 (不純物微粒子) のみを溶解除去できます。また、この処理を施したステンレス鋼は、海水環境や塩酸など厳しい腐食環境でも全く腐食しなくなることを確認しています。この技術は、構造物、医療器材、燃料電池などへの活用が期待されています。
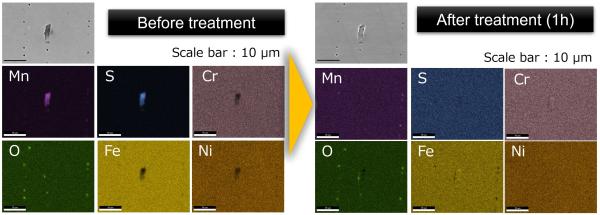
腐食を引き起こす欠陥 (マンガンと硫黄を含む微粒子) のみを選択的に除去する表面処理技術
4. 実験と計算を併用した金属材料の腐食機構解明
電気化学計測・表面分析などの実験による手法と、計算科学 (シミュレーション) の手法を併用することで、金属材料の腐食機構の解明や高耐食化を目的に研究を行っています。例えば、数値シミュレーション (有限要素解析) を用いた異種材料の共存部での腐食挙動の解析や、第一原理計算を用いた鉄鋼材料中の合金元素が耐食性におよぼす影響の解明などに取り組んでいます。
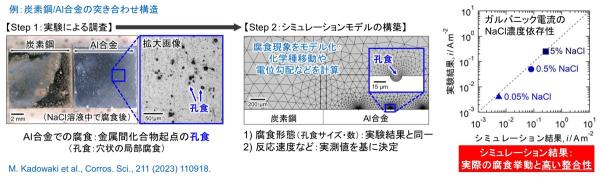
数値シミュレーションによる異種材料共存部の腐食挙動の解析
Outline
Corrosion of metal materials is one of the factors that cause structural deterioration and damage, resulting in economic loss. The Corrosion Research Group investigates the corrosion deterioration behavior at the surface and interface of metal materials in various environments, in order to solve many corrosion problems. Furthermore, through the elucidation of these mechanisms, we aim to contribute to improving the reliability and durability of metal materials in various usage environments.
Specialized Research Field
1. Advancement of atmospheric corrosion monitoring technology for steel materials and establishment of non-destructive corrosion risk prediction technology
The cost of repairing and updating aging social infrastructure is expected to become enormous in the future. In order to use these safely for a long time in the future, it is necessary to switch from the conventional corrective maintenance type to the preventive maintenance type. It is important to accurately grasp the current situation and predict risks in preventive maintenance. In this theme, we aim to improve the atmospheric corrosion rate monitoring technology for understanding the corrosion status of steel materials and to establish corrosion risk prediction technology using a simple non-destructive evaluation method.
2. Evaluation of Corrosion Behavior by using combined SKPFM-EBSD-EDS analysis
Evaluation of corrosion behavior dependent on the microstructure of structural materials is conducted by using analyses of scanning Kelvin probe force microscopy (SKPFM) as well as electron backscatter diffraction (EBSD) and energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS) in scanning microscopy. The locations of corrosion initiation can be mapped by detecting changes in surface potential in SKPFM analysis, the corrosion resistance based on crystal structure is evaluated by EBSD analysis, and the formation of inclusions and elemental segregation involved with corrosion reactions are detected by EDS analysis. The purpose of this research is to obtain a structural material design guideline with excellent corrosion resistance by combining these three different analyses.
3. Development of novel surface treatment techniques realizing extremely-enhanced corrosion resistance for metallic materials
We are developing the surface treatment techniques for improvement of stainless steel surfaces to minimize the risk of unexpected corrosion failure and accidents, enabling reliable utilization of the steels. These treatments are performed under newly-developed electric current and potential conditions in a specific treatment solution. Only the exposed defects (impurity particles) exposed on the steel surface, which are the initiation sites of localized corrosion, are successfully dissolved and removed. It has been confirmed that stainless steel reinforced by this treatment shows totally corrosion resistance even in severe corrosive environments such as artificial seawater and hydrochloric acid. This technique is expected to be used for structural materials, medical implants, and fuel cells.

The developed surface treatment that selectively removes only the defects
(manganese and sulfides inclusions) inducing localized corrosion from stainless steel surface.
4. Clarifying the corrosion mechanisms of metals by combining experimental and computational simulation techniques
We are using both experimental techniques and computational simulations to clarify the corrosion mechanisms of metals and to improve their corrosion resistance. For example, we are conducting numerical simulations based on finite element method (FEM) to analyze the corrosion behavior of dissimilar metal couples, and first-principles calculations to elucidate the effect of alloying elements on the corrosion behavior of steels.
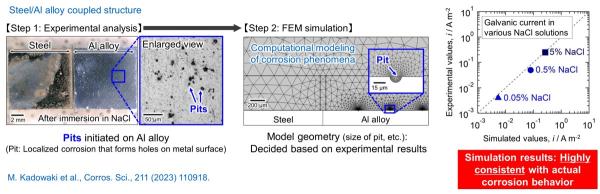
Corrosion analysis of steel/Al alloy couple using FEM simulation.




