Machine:Raman microscope/ RENISHAW
Features and Main Specifications:Laser wavelength 532 nm.
Model:
・inVia Reflex confocal Raman
・microscope
Contact:Kotaro Doi DOI.Kotaro=nims.go.jp (Please change "=" to "@")
Raman microscope
The following can be done by means of this equipment.
- Identification of rust components of metallic materials.
- Identification of inorganic compounds such as metal oxides.
- Raman mapping with a spatial resolution of approx. 1 micrometer.

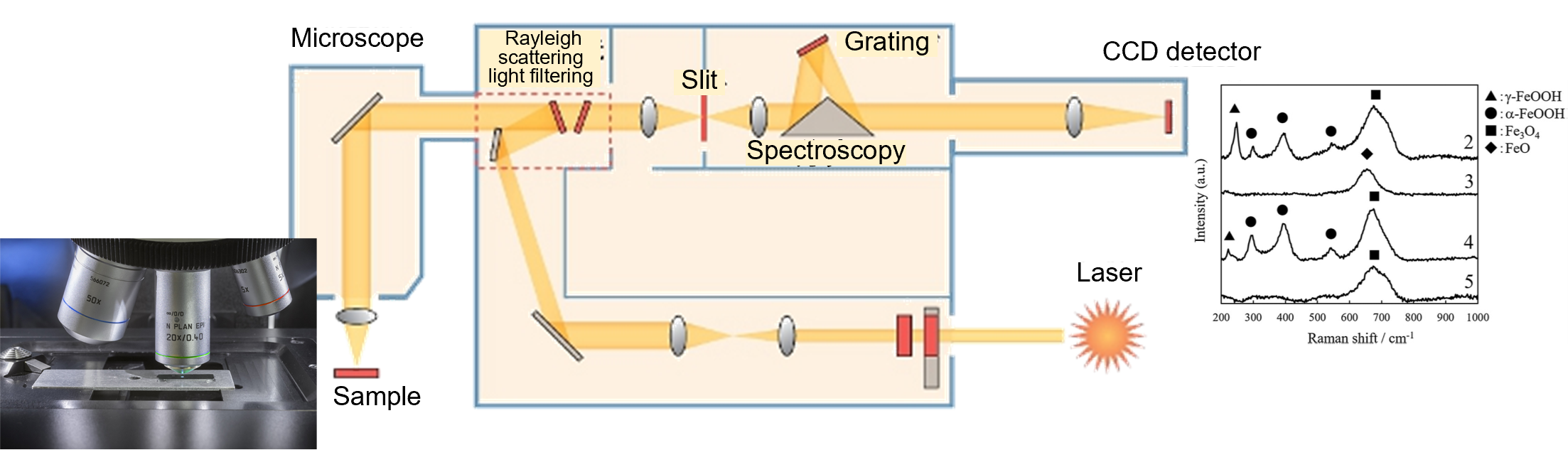
Principles of Raman spectroscopy
In the Raman microscope, a laser beam is irradiated onto a sample using an objective lens. The Raman scattering light is generated from the sample surface and is focused by the objective lens. The light is then spectrally split into Rayleigh and Raman scattering light by a spectrograph and the Raman scattering light is detected by a CCD detector to obtain Raman spectral data.
The energy difference (Raman shift) between the Rayleigh and Raman scattering light corresponds to the vibrational energy of the atoms and molecules in the irradiated material, which can be used to determine the molecular structure, crystal structure and bonding state of the material. The measurement depth is governed by the absorption of the source laser light and the Raman scattered light by the sample.
Uses: Identification of substances in solids, powders and thin films, Analysis of bonding states of compounds.